We update the price of Bitcoin (BTC/USD) in real time.
Bitcoin Chart (BTC/USD)
Interactive chart of Bitcoin (BTC/USD) so that, in addition to visualizing the progression of the price of Bitcoin, you can also do your technical analysis using the tools available in the left sidebar.
Some of these tools are trend lines, channels, fibonacci retracements, formation of triangles and wedges, etc.
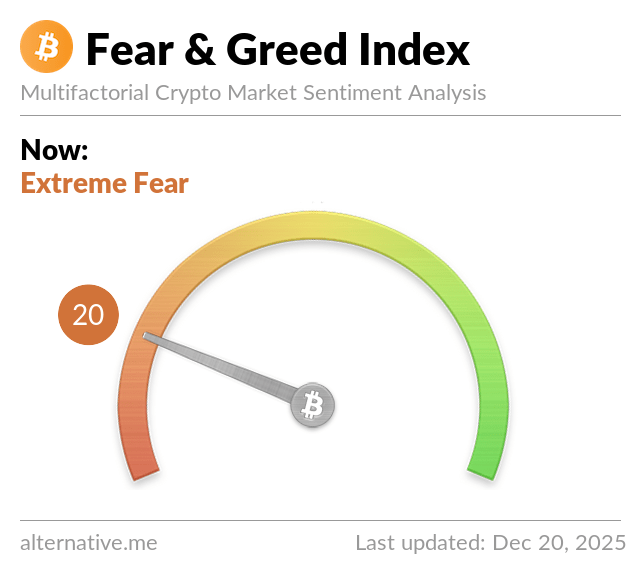
Fear and euphoria index of Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies
The Crypto Fear and Greed Index measures the emotions and sentiment driving the cryptocurrency markets.
The main purpose of this index is to prevent people from emotionally overreacting to FOMO as markets rise and people irrationally sell when they see red numbers.
Index takes its value depending on:
- Volatility (25%)
- Market Momentum/Volume (25%)
- Social networks (15%)
- Surveys (15 %)
- Domain (10%)
- Trends (10%)
Currently, the main exchanges (exchanges) of cryptocurrencies to buy/sell (either to hold or trade) Bitcoin are: Bit2Me, Binance, Coinbase, KuCoin and Bitfinex.
Latest important news related to Bitcoin (BTC) and cryptocurrencies.
Table of Contents:
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin, apart from being the first cryptocurrency, is the best known of the more than 15K cryptocurrencies (altcoins) that currently exist. And, although it presents less volatility than altcoins, it is not exempt from big changes in its price.
While high volatility can produce big profits, it hardly makes Bitcoin the best option for novice investors or people looking for a stable store of value. So it is essential to know Bitcoin before investing in it.
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency that you can buy, sell, and trade directly, without a middleman like a bank. Bitcoin creator Satoshi Nakamoto originally described the need for “an electronic payment system based on cryptographic evidence rather than trust.” All described in the Bitcoin Whitepaper.
Each and every Bitcoin transaction ever made exists on a public ledger accessible to all, making transactions difficult to reverse and difficult to falsify. That is by design: due to its decentralized nature, bitcoins are not backed by the government or any issuing institution, and there is nothing to guarantee their value other than the proof baked into the heart of the system. The reason it is worth money is simply because we as people decide that it has value, just like gold.
Since its public launch in 2009, the value of Bitcoin has increased dramatically. Although once trading below $100 per coin, the price of Bitcoin has since peaked at $69,000 (its ATH occurred in early November 2021).
Because its supply is limited to 21 million coins, many expect its price to continue to rise as time goes on, especially as institutional investors start treating it as a kind of digital gold to hedge against market volatility. and inflation.
This means that there will never be more than 21 million Bitcoin, so as its adoption in society increases, its price must inevitably continue to rise. It is nothing more than the law of supply-demand.
How does Bitcoin work?
Bitcoin is based on a distributed digital ledger called a blockchain. As its name suggests, blockchain is a linked data set, made up of units called blocks that contain information about each and every transaction.
The information that is included in the transactions are the date and time, the total value, the buyer and seller, and a unique identification code for each exchange. The entries are chained in chronological order, creating a digital chain of blocks.
Once a block is added to the blockchain, it can be accessed by anyone who wishes to view it, acting as a public ledger of cryptocurrency transactions.
The blockchain is decentralized, which means that it is not controlled by any organization. Think of it as a Google Doc where anyone can work on it, but no one owns it, and anyone with a link can contribute. And, as different people update it, your copy is also updated.
While the idea that anyone can edit the blockchain might sound risky, it is actually what makes Bitcoin trustworthy and secure. For a transaction block to be added to the Bitcoin blockchain, it must be verified by the majority of Bitcoin holders, and the unique codes used to recognize user wallets and transactions must conform to the correct encryption pattern. .
These codes are long, random numbers, making them incredibly difficult to fraudulently produce. This level of statistical randomness of blockchain verification codes, which are needed for every transaction, greatly reduces the risk of someone making fraudulent Bitcoin transactions.
What is Bitcoin mining and how does it work?
Bitcoin mining is the process of adding new transactions to the Bitcoin blockchain. It is hard work. People who choose to mine Bitcoin use a process called proof of work (PoW), deploying computers in a race to solve math puzzles that verify transactions.
To entice miners to keep competing to solve the puzzles and support the system in general, the Bitcoin code rewards miners with new Bitcoins. This is how new coins are created and new transactions are added to the blockchain.
In the early days, it was possible for the average person to mine Bitcoin, but that is no longer the case. Bitcoin’s code is made to make solving its puzzles more and more challenging over time, requiring more and more computing resources. Today, Bitcoin mining requires powerful computers and access to massive amounts of cheap electricity to be successful.
In addition, it is usually less than before. Back in 2009, when this technology first came out, every time you received a block, you got a much larger amount of Bitcoin than you do today. There are more and more transactions, so the amount you get paid for each block is less and less.
By 2140, it is estimated that all Bitcoins will have entered circulation, meaning that mining will not release new coins and instead miners may have to rely on transaction fees.
How to use your bitcoins
In Spain, other countries in Europe, the United States, Latin America, Asia,… people use Bitcoin as an alternative investment, which helps to diversify a portfolio of stocks and bonds. It can also be used to make purchases, but the number of providers that accept the cryptocurrency is still limited.
Some of the big companies that accept Bitcoin as a payment method are: Microsoft, PayPal, and Whole Foods, to name just a few. You may also find that some small local retailers or websites accept Bitcoin, but it is still difficult to find them.
You can also use a service that allows you to connect a debit card to your cryptocurrency account (wallet), which means you can use Bitcoin the same way you would use a credit card. This usually also involves a financial provider instantly converting your Bitcoin into dollars, euros or any FIAT currency.
In other countries, particularly those with less stable currencies, some people use crypto instead of their own currency.
Bitcoin provides an opportunity for people to store value without relying on a government-backed currency. It gives people the option to protect themselves in the worst case scenario. You are already seeing people in countries like Venezuela, Argentina, Zimbabwe; In highly indebted countries, Bitcoin is getting huge traction.
That said, when you use Bitcoin as a currency, whether for investment or consumption, you need to be aware of certain tax implications in your country.
Buy bitcoin
Most people buy Bitcoin through cryptocurrency exchanges. Exchanges allow you to buy, sell and hold cryptocurrencies. Setting up an account is similar to opening a brokerage account: you’ll need to verify your identity (KYC) and provide some form of funding source, such as a bank account or debit card.
Major exchanges include Bit2Me, Coinbase, Binance, Kucoin, Bitfinex. You can also buy Bitcoin at an online broker like Robinhood.
Regardless of where you buy Bitcoin, you will need a Bitcoin wallet to store it. This could be what is called a hot wallet or a cold wallet.
A hot wallet (also called an online wallet) is stored by an exchange or cloud provider. Some online wallet providers are Exodus, Electrum and Mycelium. A cold wallet (or mobile wallet) is an offline device that is used to store Bitcoin and is not connected to the Internet. Some cold wallet options are Trezor and Ledger.
Some important notes about buying Bitcoin: Although a Bitcoin has a high price, you can buy Bitcoin in fractions. You’ll also want to keep an eye out for fees, which are usually small percentages of your crypto transaction amount, but can really add up on small purchases.
Finally, keep in mind that Bitcoin purchases are not instant like many other stock purchases seem to be. Because miners must verify Bitcoin transactions, it may take at least 10-20 minutes to see your Bitcoin purchase in your account.
How to invest in Bitcoin
Just like a stock, you can buy and hold Bitcoin as an investment. No matter where you choose to hold your Bitcoin, people’s philosophies on how to invest it vary: some buy and hold for the long haul, some buy and intend to sell after a price rally, and others bet on its price going down (shorting).
Consumers can also invest in a Bitcoin mutual fund by purchasing shares of Grayscale Bitcoin Trust (GBTC), although it is currently only open to accredited investors who earn at least $200K or have a net worth of at least $1 million.
One important note though: While cryptocurrency-based funds may add diversification to cryptocurrency holdings and slightly lower risk, they still carry substantially more risk and charge much higher fees than broad-based index funds with a history of consistent returns. Investors looking to steadily increase their wealth can opt for index-based mutual and exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
Should you buy Bitcoin?
In general, many financial experts are supportive of their clients’ desire to buy cryptocurrencies, but do not recommend them unless clients express an interest.
The speculative nature of cryptocurrency leads some planners to recommend it for clients’ “secondary” investments.
In a very real sense, Bitcoin is like a single stock, and advisers would not recommend putting a significant portion of your portfolio into any one company. At best, planners suggest putting no more than 1% to 10% into Bitcoin if you are passionate about it.
Bitcoin Whitepaper
The Bitcoin white paper was the first document to outline the principles of a cryptographically secure peer-to-peer electronic payment system, which was fundamentally designed to be transparent and censorship-resistant, as well as to take financial control back from the public. individual.
At the time, the world was in the throes of a financial crisis catalyzed by excessive speculation in financial markets and banks risking millions of dollars in depositors’ money.
This document laid the foundation for what is generally considered to be the first functional digital currency powered by a distributed ledger technology called a blockchain.
One of the many innovative elements of Satoshi’s electronic payment system was that it solved the age-old “double spending” problem that plagued cashless spending. Through the implementation of time-stamped transactions that are unanimously verified by a distributed network of validators, it was no longer possible for one person to spend the same funds twice.
The white paper was released under an MIT Public License in 2008 for everyone to learn, share, and enjoy.
Below is the complete Bitcoin whitepaper document in English, published on www.bitcoin.org.
Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System
Satoshi Nakamoto
satoshin@gmx.com
www.bitcoin.org
Abstract. A purely peer-to-peer version of electronic cash would allow online payments to be sent directly from one party to another without going through a financial institution. Digital signatures provide part of the solution, but the main benefits are lost if a trusted third party is still required to revent double-spending. We propose a solution to the double-spending problem using a peer-to-peer network. The network timestamps transactions by hashing them into an ongoing chain of hash-based proof-of-work, forming a record that cannot be changed without redoing the proof-of-work. The longest chain not only serves as proof of the sequence of events witnessed, but proof that it came from the largest pool of CPU power. As long as a majority of CPU power is controlled by nodes that are not cooperating to attack the network, they’ll generate the longest chain and outpace attackers. The network itself requires minimal structure. Messages are broadcast on a best effort basis, and nodes can leave and rejoin the network at will, accepting the longest proof-of-work chain as proof of what happened while they were gone.
1. Introduction
Commerce on the Internet has come to rely almost exclusively on financial institutions serving as trusted third parties to process electronic payments. While the system works well enough for most transactions, it still suffers from the inherent weaknesses of the trust based model. Completely non-reversible transactions are not really possible, since financial institutions cannot avoid mediating disputes. The cost of mediation increases transaction costs, limiting the minimum practical transaction size and cutting off the possibility for small casual transactions, and there is a broader cost in the loss of ability to make non-reversible payments for nonreversible services. With the possibility of reversal, the need for trust spreads. Merchants must be wary of their customers, hassling them for more information than they would otherwise need. A certain percentage of fraud is accepted as unavoidable. These costs and payment uncertainties can be avoided in person by using physical currency, but no mechanism exists to make payments over a communications channel without a trusted party.
What is needed is an electronic payment system based on cryptographic proof instead of trust, allowing any two willing parties to transact directly with each other without the need for a trusted third party. Transactions that are computationally impractical to reverse would protect sellers from fraud, and routine escrow mechanisms could easily be implemented to protect buyers. In this paper, we propose a solution to the double-spending problem using a peer-to-peer distributed timestamp server to generate computational proof of the chronological order of transactions. The system is secure as long as honest nodes collectively control more CPU power than any cooperating group of attacker nodes.
2. Transactions
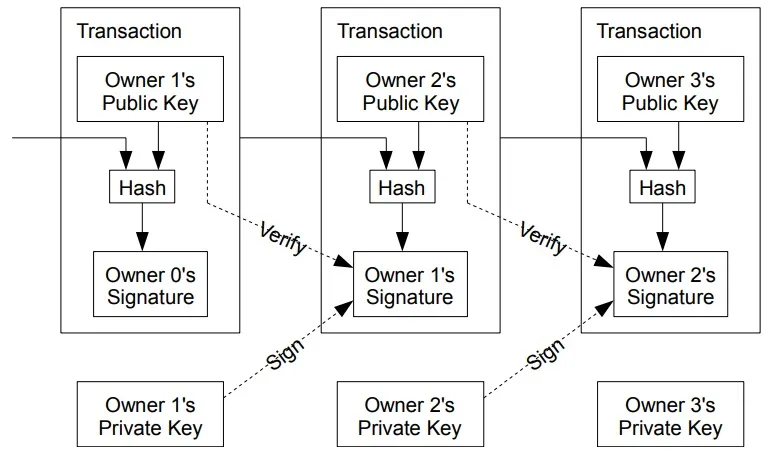
We define an electronic coin as a chain of digital signatures. Each owner transfers the coin to the next by digitally signing a hash of the previous transaction and the public key of the next owner and adding these to the end of the coin. A payee can verify the signatures to verify the chain of ownership.
The problem of course is the payee can’t verify that one of the owners did not double-spend the coin. A common solution is to introduce a trusted central authority, or mint, that checks every transaction for double spending. After each transaction, the coin must be returned to the mint to issue a new coin, and only coins issued directly from the mint are trusted not to be double-spent. The problem with this solution is that the fate of the entire money system depends on the company running the mint, with every transaction having to go through them, just like a bank.
We need a way for the payee to know that the previous owners did not sign any earlier transactions. For our purposes, the earliest transaction is the one that counts, so we don’t care about later attempts to double-spend. The only way to confirm the absence of a transaction is to be aware of all transactions. In the mint based model, the mint was aware of all transactions and decided which arrived first. To accomplish this without a trusted party, transactions must be publicly announced [1], and we need a system for participants to agree on a single history of the order in which they were received. The payee needs proof that at the time of each transaction, the majority of nodes agreed it was the first received.
3. Timestamp Server
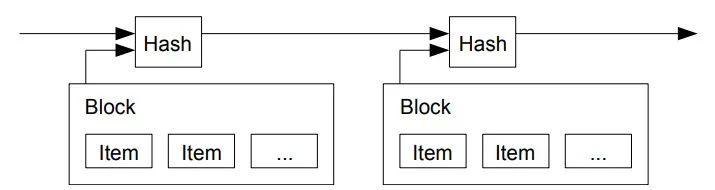
The solution we propose begins with a timestamp server. A timestamp server works by taking a hash of a block of items to be timestamped and widely publishing the hash, such as in a newspaper or Usenet post [2-5]. The timestamp proves that the data must have existed at the time, obviously, in order to get into the hash. Each timestamp includes the previous timestamp in its hash, forming a chain, with each additional timestamp reinforcing the ones before it.
4. Proof-of-work
To implement a distributed timestamp server on a peer-to-peer basis, we will need to use a proofof-work system similar to Adam Back’s Hashcash [6], rather than newspaper or Usenet posts. The proof-of-work involves scanning for a value that when hashed, such as with SHA-256, the hash begins with a number of zero bits. The average work required is exponential in the number of zero bits required and can be verified by executing a single hash.
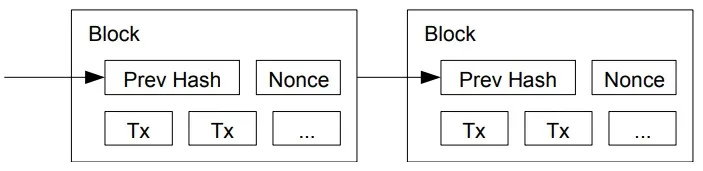
For our timestamp network, we implement the proof-of-work by incrementing a nonce in the block until a value is found that gives the block’s hash the required zero bits. Once the CPU effort has been expended to make it satisfy the proof-of-work, the block cannot be changed without redoing the work. As later blocks are chained after it, the work to change the block would include redoing all the blocks after it.
The proof-of-work also solves the problem of determining representation in majority decision making. If the majority were based on one-IP-address-one-vote, it could be subverted by anyone able to allocate many IPs. Proof-of-work is essentially one-CPU-one-vote. The majority decision is represented by the longest chain, which has the greatest proof-of-work effort invested in it. If a majority of CPU power is controlled by honest nodes, the honest chain will grow the fastest and outpace any competing chains. To modify a past block, an attacker would have to redo the proof-of-work of the block and all blocks after it and then catch up with and surpass the work of the honest nodes. We will show later that the probability of a slower attacker catching up diminishes exponentially as subsequent blocks are added.
To compensate for increasing hardware speed and varying interest in running nodes over time, the proof-of-work difficulty is determined by a moving average targeting an average number of blocks per hour. If they’re generated too fast, the difficulty increases.
5. Network
The steps to run the network are as follows:
1) New transactions are broadcast to all nodes.
2) Each node collects new transactions into a block.
3) Each node works on finding a difficult proof-of-work for its block.
4) When a node finds a proof-of-work, it broadcasts the block to all nodes.
5) Nodes accept the block only if all transactions in it are valid and not already spent.
6) Nodes express their acceptance of the block by working on creating the next block in the chain, using the hash of the accepted block as the previous hash.
Nodes always consider the longest chain to be the correct one and will keep working on extending it. If two nodes broadcast different versions of the next block simultaneously, some nodes may receive one or the other first. In that case, they work on the first one they received, but save the other branch in case it becomes longer. The tie will be broken when the next proofof-work is found and one branch becomes longer; the nodes that were working on the other branch will then switch to the longer one.
New transaction broadcasts do not necessarily need to reach all nodes. As long as they reach many nodes, they will get into a block before long. Block broadcasts are also tolerant of dropped messages. If a node does not receive a block, it will request it when it receives the next block and realizes it missed one.
6. Incentive
By convention, the first transaction in a block is a special transaction that starts a new coin owned by the creator of the block. This adds an incentive for nodes to support the network, and provides a way to initially distribute coins into circulation, since there is no central authority to issue them. The steady addition of a constant of amount of new coins is analogous to gold miners expending resources to add gold to circulation. In our case, it is CPU time and electricity that is expended. The incentive can also be funded with transaction fees. If the output value of a transaction is less than its input value, the difference is a transaction fee that is added to the incentive value of the block containing the transaction. Once a predetermined number of coins have entered circulation, the incentive can transition entirely to transaction fees and be completely inflation free.
The incentive may help encourage nodes to stay honest. If a greedy attacker is able to assemble more CPU power than all the honest nodes, he would have to choose between using it to defraud people by stealing back his payments, or using it to generate new coins. He ought to find it more profitable to play by the rules, such rules that favour him with more new coins than everyone else combined, than to undermine the system and the validity of his own wealth.
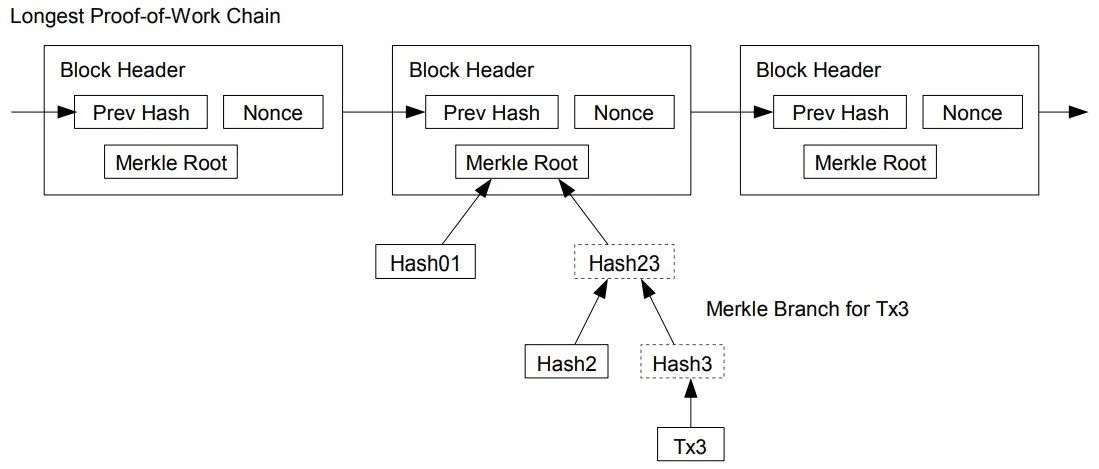
7. Reclaiming Disk Spaxe
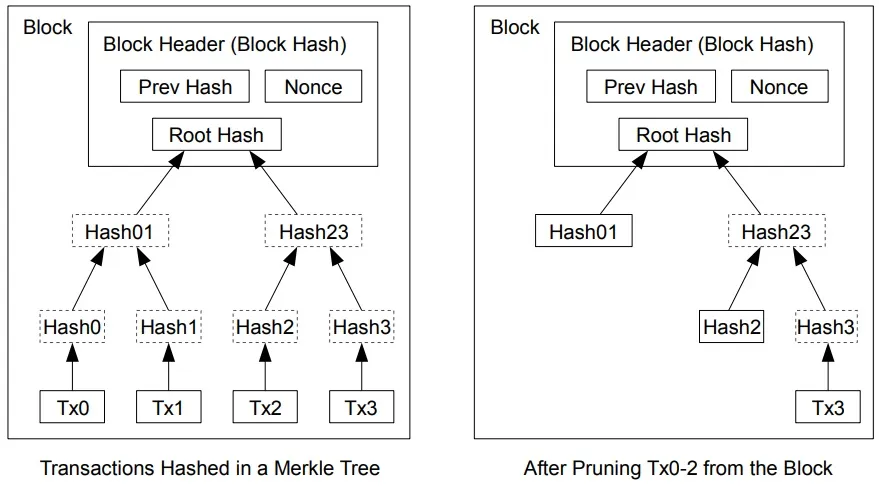
Once the latest transaction in a coin is buried under enough blocks, the spent transactions before it can be discarded to save disk space. To facilitate this without breaking the block’s hash, transactions are hashed in a Merkle Tree [7][2][5], with only the root included in the block’s hash. Old blocks can then be compacted by stubbing off branches of the tree. The interior hashes do not need to be stored.
A block header with no transactions would be about 80 bytes. If we suppose blocks are generated every 10 minutes, 80 bytes * 6 * 24 * 365 = 4.2MB per year. With computer systems typically selling with 2GB of RAM as of 2008, and Moore’s Law predicting current growth of
1.2GB per year, storage should not be a problem even if the block headers must be kept in memory.
8. Simplified Payment Verification
It is possible to verify payments without running a full network node. A user only needs to keep a copy of the block headers of the longest proof-of-work chain, which he can get by querying network nodes until he’s convinced he has the longest chain, and obtain the Merkle branch linking the transaction to the block it’s timestamped in. He can’t check the transaction for himself, but by linking it to a place in the chain, he can see that a network node has accepted it, and blocks added after it further confirm the network has accepted it.
As such, the verification is reliable as long as honest nodes control the network, but is more vulnerable if the network is overpowered by an attacker. While network nodes can verify transactions for themselves, the simplified method can be fooled by an attacker’s fabricated
transactions for as long as the attacker can continue to overpower the network. One strategy to protect against this would be to accept alerts from network nodes when they detect an invalid block, prompting the user’s software to download the full block and alerted transactions to confirm the inconsistency. Businesses that receive frequent payments will probably still want to run their own nodes for more independent security and quicker verification.
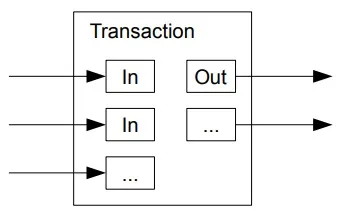
9. Combining and Splitting Value
Although it would be possible to handle coins individually, it would be unwieldy to make a separate transaction for every cent in a transfer. To allow value to be split and combined, transactions contain multiple inputs and outputs. Normally there will be either a single input
from a larger previous transaction or multiple inputs combining smaller amounts, and at most two outputs: one for the payment, and one returning the change, if any, back to the sender.
It should be noted that fan-out, where a transaction depends on several transactions, and those transactions depend on many more, is not a problem here. There is never the need to extract a complete standalone copy of a transaction’s history.
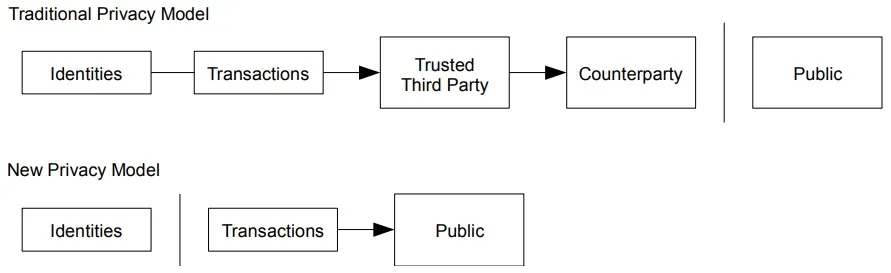
10. Privacy
The traditional banking model achieves a level of privacy by limiting access to information to the parties involved and the trusted third party. The necessity to announce all transactions publicly precludes this method, but privacy can still be maintained by breaking the flow of information in another place: by keeping public keys anonymous. The public can see that someone is sending an amount to someone else, but without information linking the transaction to anyone. This is similar to the level of information released by stock exchanges, where the time and size of individual trades, the “tape”, is made public, but without telling who the parties were.
As an additional firewall, a new key pair should be used for each transaction to keep them from being linked to a common owner. Some linking is still unavoidable with multi-input transactions, which necessarily reveal that their inputs were owned by the same owner. The risk
is that if the owner of a key is revealed, linking could reveal other transactions that belonged to the same owner..
11. Calculations
We consider the scenario of an attacker trying to generate an alternate chain faster than the honest chain. Even if this is accomplished, it does not throw the system open to arbitrary changes, such as creating value out of thin air or taking money that never belonged to the attacker. Nodes are not going to accept an invalid transaction as payment, and honest nodes will never accept a block containing them. An attacker can only try to change one of his own transactions to take back money he recently spent.
The race between the honest chain and an attacker chain can be characterized as a Binomial Random Walk. The success event is the honest chain being extended by one block, increasing its lead by +1, and the failure event is the attacker’s chain being extended by one block, reducing the gap by -1.
The probability of an attacker catching up from a given deficit is analogous to a Gambler’s Ruin problem. Suppose a gambler with unlimited credit starts at a deficit and plays potentially an infinite number of trials to try to reach breakeven. We can calculate the probability he ever reaches breakeven, or that an attacker ever catches up with the honest chain, as follows [8]:
p = probability an honest node finds the next block
q = probability the attacker finds the next block
qz = probability the attacker will ever catch up from z blocks behind
Given our assumption that p > q, the probability drops exponentially as the number of blocks the attacker has to catch up with increases. With the odds against him, if he doesn’t make a lucky lunge forward early on, his chances become vanishingly small as he falls further behind.
We now consider how long the recipient of a new transaction needs to wait before being sufficiently certain the sender can’t change the transaction. We assume the sender is an attacker who wants to make the recipient believe he paid him for a while, then switch it to pay back to himself after some time has passed. The receiver will be alerted when that happens, but the sender hopes it will be too late.
The receiver generates a new key pair and gives the public key to the sender shortly before signing. This prevents the sender from preparing a chain of blocks ahead of time by working on it continuously until he is lucky enough to get far enough ahead, then executing the transaction at that moment. Once the transaction is sent, the dishonest sender starts working in secret on a parallel chain containing an alternate version of his transaction.
The recipient waits until the transaction has been added to a block and z blocks have been linked after it. He doesn’t know the exact amount of progress the attacker has made, but assuming the honest blocks took the average expected time per block, the attacker’s potential progress will be a Poisson distribution with expected value:
To get the probability the attacker could still catch up now, we multiply the Poisson density for each amount of progress he could have made by the probability he could catch up from that point:
Rearranging to avoid summing the infinite tail of the distribution…
Converting to C code…
#
include <math.h>
double AttackerSuccessProbability(double q, int z)
{
double p = 1.0 - q;
double lambda = z * (q / p);
double sum = 1.0;
int i, k;
for (k = 0; k <= z; k++)
{
double poisson = exp(-lambda);
for (i = 1; i <= k; i++)
poisson *= lambda / i;
sum -= poisson * (1 - pow(q / p, z - k));
}
return sum;
}Running some results, we can see the probability drop off exponentially with z.
Solving for P less than 0.1%…
12. Conclusion
We have proposed a system for electronic transactions without relying on trust. We started with the usual framework of coins made from digital signatures, which provides strong control of ownership, but is incomplete without a way to prevent double-spending. To solve this, we proposed a peer-to-peer network using proof-of-work to record a public history of transactions that quickly becomes computationally impractical for an attacker to change if honest nodes control a majority of CPU power. The network is robust in its unstructured simplicity. Nodes work all at once with little coordination. They do not need to be identified, since messages are not routed to any particular place and only need to be delivered on a best effort basis. Nodes can leave and rejoin the network at will, accepting the proof-of-work chain as proof of what happened while they were gone. They vote with their CPU power, expressing their acceptance of valid blocks by working on extending them and rejecting invalid blocks by refusing to work on them. Any needed rules and incentives can be enforced with this consensus mechanism.
Disclaimer: The content and links provided in this article are for informational purposes only. islaBit does not offer legal, financial or investment recommendations or advice, nor does it replace the due diligence of each interested party. islaBit does not endorse any investment offer or the like promoted here.